10 gout facts
In this article, we will describe 10 facts about gout.
1. What is gout?
Gout is a form of arthritis that develops when uric acid crystals build up in the body, and deposit needle-shaped crystals in and around the joint – leading to inflammation and joint damage.
90% of gout attacks occur in a single joint. The most common symptom is sudden, severe pain, swelling and redness often in the big toe; but gout can affect other joints as well – such as the ankles, knees, wrists, and fingers.

Classic gout in the big toe
2. Cause of gout – uric acid
Gout is due to high uric acid levels. Uric acid is a waste product formed from the breakdown of purines, which are substances found in many foods and human cells. Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood and passes through the kidneys into the urine.
3. Prevalence
Gout is more common in men than in women. It usually happens during middle age, but younger people can get gout.
Postmenopausal women are also at increased risk due to changes in hormone levels that affect uric acid metabolism.
4. Risk factors
Risk factors for gout include:
- Diet high in purines (red meat, seafood, sweetened drinks)
- Alcohol consumption (especially beer)
- Family history (there is a genetic component)
- Obesity
- Certain medical conditions (high blood pressure, chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetes)
- Medications that increase uric acid levels (see below).
Note. Rare genetic conditions (Kelley-Seegmiller syndrome or Lesch-Nyhan syndrome) can cause gout as they lead to increased uric acid levels.
5. Medications that can lead to gout
Some medications can increase your risk of developing gout, such as:
- Diuretics (water tablets)
- Low-dose aspirin
- Ciclosporin – which is an immunosuppressant for people who have organ transplants and is approved to treat some autoimmune diseases.
Note. Please don’t stop these drugs with discussing with your doctor.
6. Symptoms
Gout attacks often begin at night and can last for a week or two. Symptoms include intense joint pain, inflammation, and redness.
Some people may have frequent flare-ups, while others may not have another episode for years. However, over time, if left untreated, your episodes may happen more often and last longer.
7. Chronic gout
Without treatment, gout can become chronic, leading to joint damage and the formation of tophi, which are large deposits of uric acid crystals that can cause visible lumps under the skin.
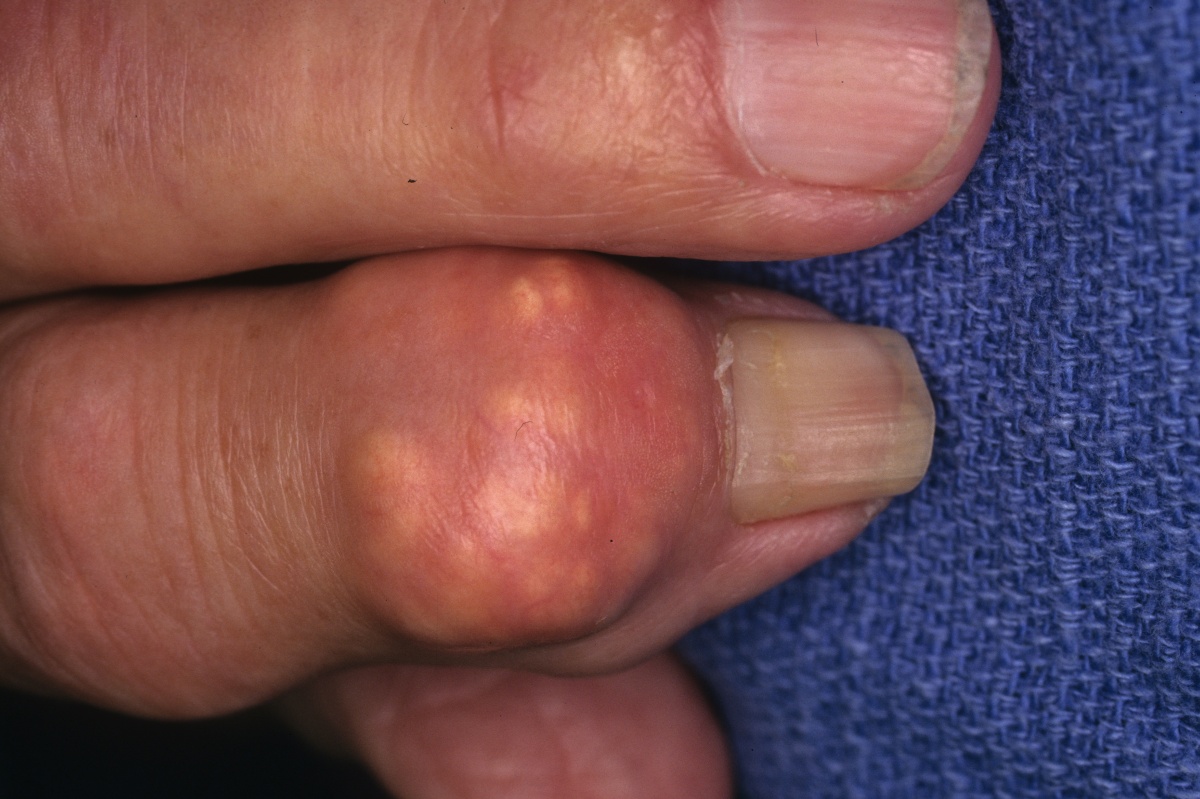
Gouty tophi
8. Diagnosis
If gout has a typical pattern, it can be diagnosed through a combination of medical history and physical examination. It may not need many (any) tests.
But if doctors are unsure, they may do tests, such as:
- Taking a small amount of fluid from your joint (joint aspiration) – doctors will look at the fluid under a special microscope to see if it has uric acid crystals
- An x-ray of your joint to look for bone changes that are common in gout
- An ultrasound to look for uric acid crystals inside your joint
- A blood test to check the level of uric acid. These are not 100% reliable. Your uric acid level may not be that high even if you have gout; and you can have high levels of uric acid, and no gout.
9. Treatment
Treatment includes medication to reduce pain and inflammation in attacks (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine, corticosteroids); and medication to prevent attacks (by lower uric acid levels, e.g. allopurinol, febuxostat).
10. Lifestyle changes
Managing gout often involves lifestyle changes, such as reducing the intake of purine-rich foods, avoiding alcohol, maintaining a healthy weight and staying hydrated – to help prevent uric acid crystal formation.
Oh yes. Did you know? ..
The white chalky substance in bird droppings is uric acid. You know what it does to your car’s paintwork, imagine what it can do to your joints?!
Summary
We have described 10 facts about gout. We hope it has been helpful.
Last Reviewed on 29 May 2024
