What are 10 important common infections?
In this article we go through what are 10 important common infections. The choice below is slightly arbitrary. Many others are also important. A bit of background first.

Coughing and fever can be caused by many, many organisms – from a minor cold virus to pulmonary TB.
What is an infection?
An infection occurs when a microorganism — such as bacteria, fungi, or a virus — enters a person’s body and causes harm. In many cases, the immune system can stop these pathogens from multiplying in the body. If not, serious damage can result.
The microorganism uses that person’s body to sustain itself, reproduce, and colonise. These infectious microscopic organisms are known as pathogens, and they can multiply quickly.
How can infections spread?
They can spread in several different ways, including through:
- Skin contact
- Transfer of bodily fluids
- Contact with faeces
- Ingesting contaminated food or water
- Inhaling airborne particles or droplets
- Touching an object that a person carrying the pathogen has also touched.
So. What are 10 important common infections? (in alphabetical order)?
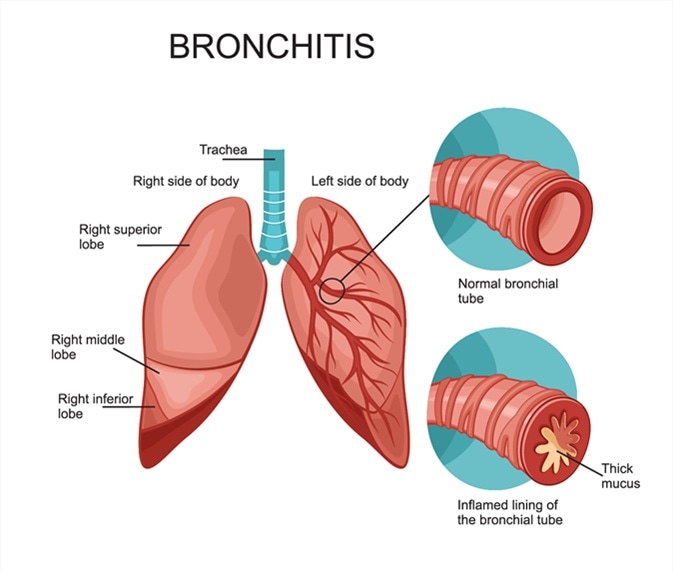
1. Bronchitis
A bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi. This causes a cough, and sputum. They are usually caused by a virus and will get better with no treatment. It is the commonest ‘upper respiratory tract infection (URTI)’. The chest x-ray will normally be normal.
2. Common colds and influenza
Influenza (flu) and the common cold are both contagious respiratory illnesses, but they are caused by different viruses. Flu is caused by influenza viruses only, whereas the common cold can be caused by a number of different viruses, including rhinoviruses, parainfluenza, and seasonal coronaviruses.
Seasonal coronaviruses should not be confused with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Because flu and the common cold (and COVID-19) have similar symptoms, it can be difficult to tell the difference between them based on symptoms alone. In general, flu is worse than the common cold, and symptoms are typically more intense and begin more abruptly.
Colds are usually milder than flu. People with colds are more likely to have a runny or stuffy nose than people who have flu. Colds generally do not result in serious health problems, such as pneumonia, bacterial infections, or hospitalisation. Flu can have serious associated complications.
3. Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the lining of the eye and eyelid – known as ‘pink (or red) eye’. The whites of the eye appear pink and may have a sticky discharge.

Conjunctivitis has three major groups of causes:
- Infective conjunctivitis – a bacterial or viral infection. This can be highly contagious
- Allergic conjunctivitis – an allergic reaction to a substance such as pollen or dust mites
- Irritant (or chemical) conjunctivitis – the eye coming into contact with things that can irritate the conjunctiva, such as shampoo or chlorinated water, or a loose eyelash rubbing against the eye.
4. COVID-19
COVID-19 is the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that emerged in December 2019.
5. Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis is a very common condition that causes diarrhoea and vomiting. It is usually caused by a bacterial or viral tummy bug, that can be related to food. It affects people of all ages, but is particularly common in young children. Most cases in children are caused by a virus called rotavirus.
It can be anything from a mild illness that lasts 24h to a life-threatening one, especially in the frail elderly.
6. HIV/AIDS
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. If HIV is not treated, it can lead to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). There is currently no effective cure. Once people get HIV, they have it for life. But with proper medical care, HIV can be controlled, and many patients can live a near normal life now.
7. Malaria
Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites. Four Plasmodium species (Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium malariae) give disease in humans, and humans are their only relevant reservoir. It can present in many ways, from a mild chronic disease, to an acute life-threatening illness.
8. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection of one or both of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It is a serious infection in which the air sacs fill with pus and other liquid. It can be diagnosed if there are typical symptoms associated with new chest x-ray shadowing. There are two main types:
- Lobar pneumonia affects one or more sections (lobes) of the lungs
- Bronchial pneumonia (also known as bronchopneumonia) affects patches throughout both lungs.
9. Sore throat
Sore throats are usually caused by viruses (like cold, flu or COVID-19). Occasionally they can be caused by bacteria. Most get better with no treatment (and no antibiotics).
A sore throat can also be caused by:
- Laryngitis
- Pharyngitis
- Tonsillitis
- Strep A throat (a bacterial throat infection, caused by Strep A bacterium)
- Glandular fever (Epstein-Barr Virus, EBV).
10. Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis (TB) is a highly infectious bacterial disease that mostly affects the lungs. But it can affect any part of the body, including the glands, bones and nervous system.
It can live in your body for years before causing symptoms. TB is a serious condition, but can be cured with proper treatment.
Other infections (also in alphabetical order). These are also important infections.
Bronchiolitis – is a common lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) that affects babies and children under 2. It’s usually mild and can be treated at home, but it can be serious. Bronchiolitis is different from bronchitis, which causes a cough with lots of mucus and can affect people of all ages.
Clostridium difficile (‘C diff’) – is a ‘superbug’ type of bacteria that can cause diarrhoea. It often affects people who have been taking antibiotics.
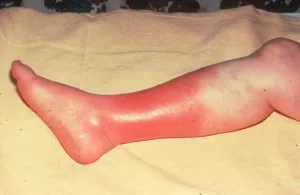
Cellulitis – is an infection caused by bacteria getting into the deeper layers of your skin. The main symptom of cellulitis is a painful, red, hot, swollen area of skin – usually on the lower leg. Cellulitis needs to be treated with antibiotics, sometimes intravenous. It can be serious if it is not treated quickly.
Chickenpox – is a mild and common childhood illness, but it can also occur in adults and is occasionally serious. Shingles is a painful rash caused by the chickenpox virus.
Chlamydia – is a common sexually-transmitted disease, STD.
Ebola virus – is a rare and often fatal viral illness.
Genital herpes – is a viral STD spread by skin-to-skin contact – e.g. through kissing or foreplay.
Gonorrhoea – is a bacterial STD, also known as ‘the clap’. Gonorrhoea often has no symptoms. It is very treatable.
Hepatitis B – is a long-term viral infection of the liver, that can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer; and in some cases, the need for a liver transplant. There are many other liver viruses including Hepatitis A and C.
Impetigo – is a highly contagious skin infection that causes sores and blisters. It is very common and affects mainly children.
Measles – is a highly infectious viral disease, spread from person to person via droplets in the air. It is best prevented by the MMR (Mumps-Measles-Rubella) vaccination.
Mumps – is a contagious viral infection, most common in children between 5 and 15 years. It is best prevented by the MMR vaccination.
Rubella – also known as German measles, is best prevented by the MMR vaccination.
Sinusitis – is when the hollow spaces in the bones of your face become inflamed. Sinusitis is a common symptom for colds and the flu and it can be difficult to diagnose.
Syphilis – is a bacterial STD that can cause serious health problems if left untreated. However, syphilis is easy to cure if found early.
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
There are different types of UTI, and the symptoms are different. The doctors name for the type of infection, depends on which part of the urinary tract is affected, e.g.
- Kidney = pyelonephritis – causing pain in the back/side of tummy
- Bladder = cystitis – lower tummy pain at the front, burning when you wee, and weeing more frequently
- Urethra = urethritis – burning when you wee, and weeing more frequently
- Prostate = prostatitis (men only) – pain in genital area.
Most common causative organism is E Coli.
Whooping cough (pertussis) – is a contagious bacterial infection and can be serious in babies.
Some other infections: diphtheria, encephalitis, hand, foot, and mouth disease, infective endocarditis, Lyme disease, meningitis, osteomyelitis, otitis media, pericarditis, poliomyelitis (polio), ringworm, Rocky mountain spotted fever, septic arthritis, tetanus and West Nile virus.
Summary
We have described 10 important common infections. The choice is slightly arbitrary. Other infections listed above are also important. We hope it has been helpful.
Last Reviewed on 9 March 2024
