What is prednisolone?
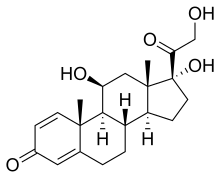
- Type of drug: corticosteroid (and synthetic version of cortisol)
- Use: immunosuppressant after kidney transplant; anti-inflammatory; other autoimmune disease
- Dose: 5 mg alternate days to 80 mg once a day (for short periods); maintenance dose is 5 mg once a day
- Side-effects:
- Diabetes; osteoporosis; increased appetite
- Cushing’s syndrome: hypertension; moon face; weight gain and central obesity; proximal muscle weakness; hypokalaemia/hypernatraemia
- Adrenal suppression (leading to Addisonian crisis if withdrawn too quickly)
- Thin skin; acne; striae; cataracts
- Altered mood; psychotic illness
- Infections; TB reactivation.
- Monitor: glucose; potassium/sodium; BP; DEXA scan alternate years.
Note 1. As with all immunosuppression, skin protection (against skin cancer) is important
Note 2. If needed to be given IV, hydrocortisone is used. 5 mg of oral prednisolone is equivalent to 20 mg of IV (or oral) hydrocortisone
Note 3. If you take prednisolone, you should wear a medical alert tag (or carry an ID card) stating that you take prednisolone. This is to alert doctors about the possibility of an Addisonian crisis.
Other resources
CKD drug side-effects
CKD patient information (CKD Explained’s 30+ core articles about CKD)
Prednisolone (BNF)
Renal transplantation (UHCW patient information)
Review article: Hodgens, 2023
Last Reviewed on 5 May 2024
