What is renal vasculitis?
Renal vasculitis is a group of rare autoimmune diseases that involve inflammation of the blood vessels (that is what vasculitis means) in the kidneys. These conditions are characterised by the body’s immune system mistakenly attacking the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to inflammation and damage to the renal tissue.
Types of vasculitis
There are several types that can affect the kidney. They affect different sized arteries, which can be anywhere from large ones near to the heart, to tiny ones deep inside the kidneys. For example, Takayasu’s Disease affects the aorta (main blood vessel from the heart); whereas Henoch-Schönlein Purpura, HSP) affects the tiny arteries inside the kidney – as shown in this diagram.
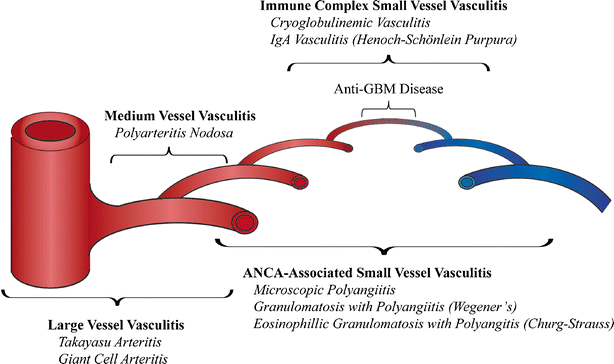
As shown in this diagram, there are many types of vasculitis that can affect the kidneys. And they vary in what symptoms they lead to, and severity. Types of renal vasculitis include:
- Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA). Formerly known as Wegener’s Granulomatosis, GPA is a severe form of vasculitis that usually affects the upper respiratory tract (including the nose), lungs, and kidneys. It can cause inflammation of small to medium-sized blood vessels in the kidneys (and airways), leading to kidney damage. Patients often have anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibodies (ANCAs).
- Microscopic Polyangiitis (MPA). MPA is another type of vasculitis that primarily affects small blood vessels, including those in the kidneys. It can cause kidney damage and can be associated with symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, and skin rashes. It is also often linked to ANCA antibodies.
- Churg-Strauss Syndrome (CSS). CSS is a rare type of vasculitis that affects small and medium-sized blood vessels. It is often associated with asthma and eosinophilia (an increased number of a type of white blood cell called eosinophils in the blood). Kidney involvement can occur in CSS.
- Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP). HSP is a vasculitis that primarily affects children. It involves inflammation of small blood vessels and can affect various organs, including the kidneys. It is characterised by a skin rash, joint pain, abdominal pain, and kidney problems.
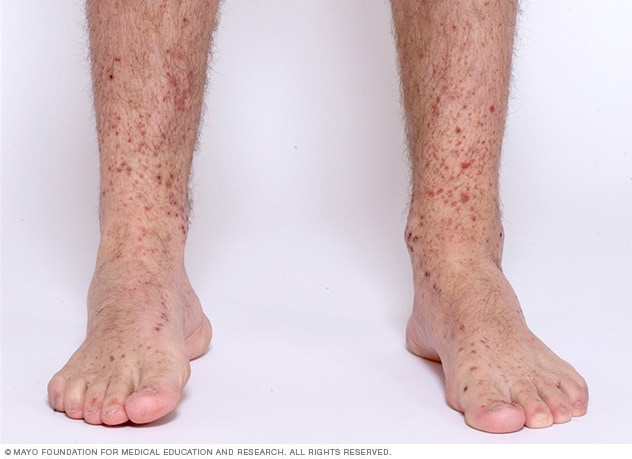
Typical rash of Henoch-Schönlein Purpura (HSP)
Symptoms
Symptoms of renal vasculitis vary depending on the specific type and severity of the condition but may include:
- Haematuria (blood in the urine)
- Proteinuria (protein in the urine). If severe this can present as nephrotic syndrome
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
- Skin rashes – and nail and nailbed abnormalities

- Abdominal pain
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD). This can lead to stage 5 CKD and the need for dialysis and/or a kidney transplant
- Acute kidney injury (AKI). This may be severe and require urgent dialysis. AKI can also be part of a ‘pulmonary-renal syndrome’. This means AKI that is linked to bleeding in the nose or lungs, which leads to severe nose bleeds or coughing up blood
- Many other symptoms. This diagram shows how a vasculitis can affect any organ.

Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves a combination of clinical assessment by a specialist kidney doctor (nephrologist), blood and urine tests, imaging studies (such as a renal ultrasound), and a kidney biopsy – to confirm the presence of vasculitis and assess the extent of kidney damage.
Treatment
Treatment for renal vasculitis usually involves medication to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation, such as steroids and immunosuppressive drugs. In some cases, if kidney function is severely compromised, a special technique called plasma exchange (a bit like dialysis), and/or dialysis, may be needed. Dialysis may be temporary or permanent. A kidney transplant may be also be needed later.
The diagnosis is quite often missed partly as these conditions are rare, and partly as symptoms can be non-specific. However it is important to note that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to minimise kidney damage and improve long-term outcome.
Summary
We have described what is renal vasculitis. We hope it has been helpful.
Last Reviewed on 23 October 2023
