What is the urinary tract?
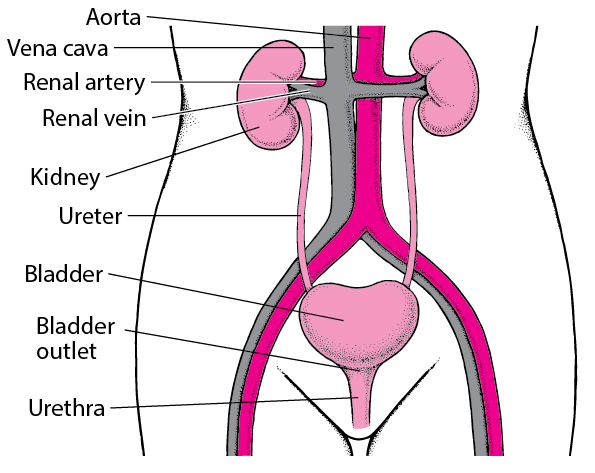
The urinary tract is the body’s drainage system for removing urine, which contains wastes and extra water. For normal urination (weeing) to occur, all body parts in the urinary tract need to work together, and in the correct order.
The urinary tract includes two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder, and a urethra.
Kidneys
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine, just below the rib cage. They are about the size of your palm: 12 (10-14) cm long, 6 cm wide and 3 cm deep, and weigh 150g.
The right kidney is slightly lower, as it is pushed down by the liver. Click here to read more about where the kidneys are located.
Note: Most people are born with two kidneys but 1 in 1000 people are born with one. They will have normal renal function and do not go into CKD unless a disease process happens. Click here to read more about the effects of living with one kidney.
The kidneys filter (and clean) your blood 35x a day, with a blood volume of 5 litres. Even though 180L are filtered, most of the filtered liquid is put back (reabsorbed) into the blood as only 2L of urine emerge each day – if you drink 2.5L a day.
Ureters
These are thin tubes of muscle that connect your kidneys to your bladder and carry urine to the bladder.
Bladder
The bladder is a hollow, triangular-shaped muscular organ located in the lower abdomen (the pelvis). Its function is to act as a reservoir for urine (expanding as it fills up), before it is removed from the body through urination (weeing). Average adult bladder volume is 300 (200-400) mls – i.e. quite small – a can of coke.
When your bladder is full, nerve signals tell you to empty it. The urinary sphincter opens, and urine passes into your urethra.
Although you do not control how your kidneys function, you have some control when to empty your bladder.
Urethra
Your urethra is a thin tube at the bottom of the bladder that carries urine out of your body, when you have a wee (pee).
Men have a urethra that ends at the tip of the penis. Women have a much shorter urethra that ends at the vulva. A shorter urethra means it’s easier for bacteria from outside the body to get into the bladder and cause urinary tract infections.
Prostate (men only)
The prostate is a gland below the bladder and in front of the rectum in men. It adds fluid to semen, and its muscles help push semen through your urethra.
Summary
We have described what is the urinary tract. All parts of the urinary tract – the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra (and prostate in men) – work together to urinate normally. We hope it has been helpful.
Last Reviewed on 15 January 2024
